How Solenoid Valve Work. We’ll discuss how Solenoid Valves are constructed and how they work in a typical mechanical system. We’ll explain where they’re commonly used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, and why.
If you prefer to watch the video of this presentation, scroll to the bottom or click this link How Solenoid Valves Work
The main purpose of a solenoid valve is to automatically control the flow of fluids and gases. Solenoid valves use electromagnetism to electrically control the opening and closing of valves. They serve an important function in the automatic control of refrigerants, water, natural gas and other liquids in the HVACR industry.
Checkout these Solenoid Valves hereWhere are Solenoid Valves located?
Solenoid valves are in many systems besides the HVAC industry, but we’ll keep our discussion to the Mechanical Construction Trades. Here are some examples of where you might find solenoid valves.
Water-Source Heat Pumps and AC Units
Various energy codes require that flow to a water-cooled heat pump or AC unit be shut off when not operating during normal business hours. This prevents additional pressure drop on the pump when the water-cooled Air Conditioner isn’t operating. The condenser water flow to the non-operating compressor is stop by the controls sending a signal to the solenoid valve to close.
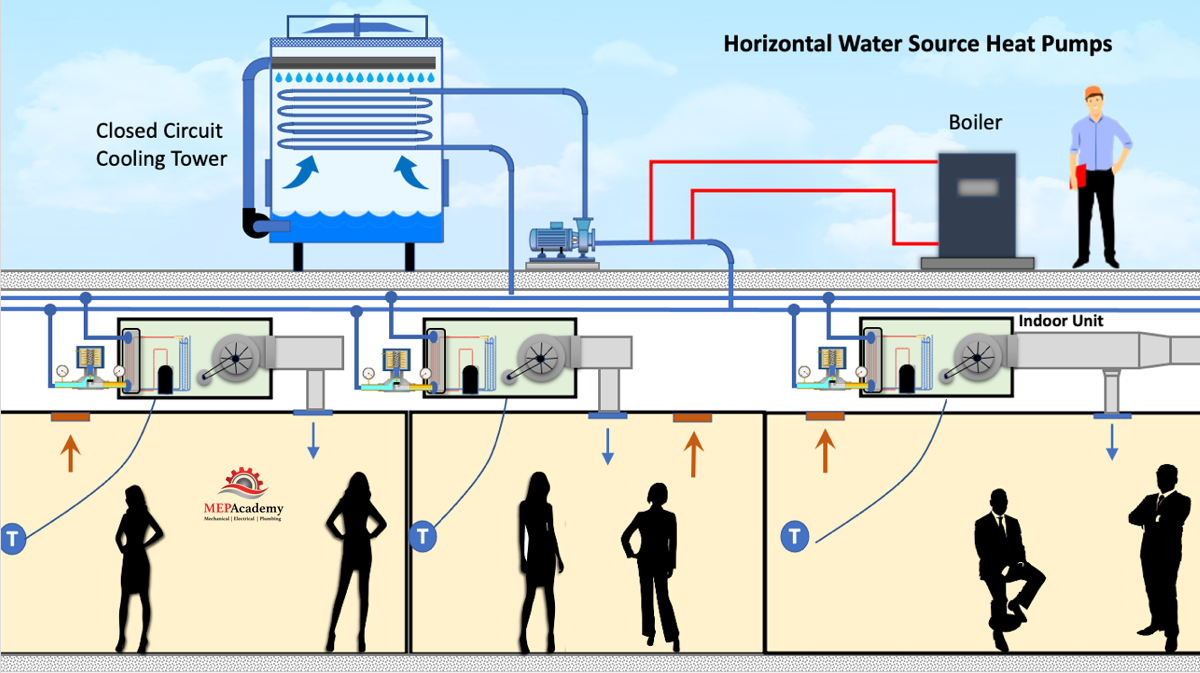
ASHRAE 90.1 2019, section 6.5.4.5.1 states “Each hydronic heat pump and water-cooled unitary air conditioner shall have a two-position automatic valve interlocked to shut off water flow when the compressor is off”.

Refrigerant Pump Down
Solenoid valves are used for the automatic pump down of refrigerant systems. This is done by placing a solenoid valve in the liquid line before the expansion valve. See our other video for explanation on How Electronic Thermal Expansion Valves Work.
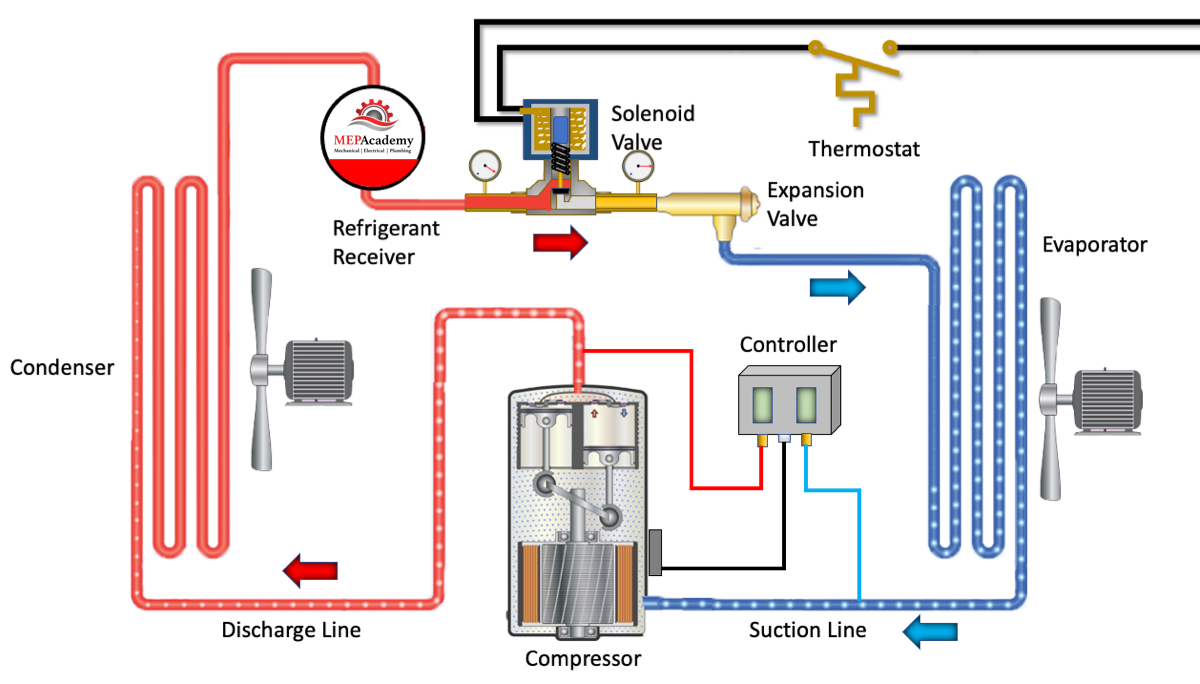
When the thermostat is closed upon a rise in temperature the solenoid is energized causing it to open and allow refrigerant to flow through the normally closed solenoid valve to the expansion valve. The refrigerant entering the evaporator causes a rise in pressure that triggers the controller to turn the compressor on. When the thermostat is satisfied and cooling is no longer required, it stops the flow of electricity to the solenoid valve, causing it to close.
The compressor keeps running, pulling the refrigerant out of the low side and into the high side liquid receiver.
When the suction pressure gets too low, before it reaches a vacuum, the low-pressure safety switch will shut off the compressor to prevent it from burning out. The pressure-sensitive controller will turn on and off the compressor based on suction pressure.
Checkout these Solenoid Valves hereWhen choosing solenoid valves for refrigerant systems, the engineer will use the refrigerant type, the tonnage, and the Maximum Operating Pressure Differential as the selection criteria. Manufacturers provide tables for selection of their solenoid valves.
Hot Gas Bypass
To prevent the evaporator coil from freezing during low load conditions, a bypass is routed from the hot gas discharge of the compressor to the low side of the system right before entering the evaporator. Bypass is controlled by a Hot Gas Bypass Valve that maintains a minimum evaporator pressure to prevent freezing of the coil.
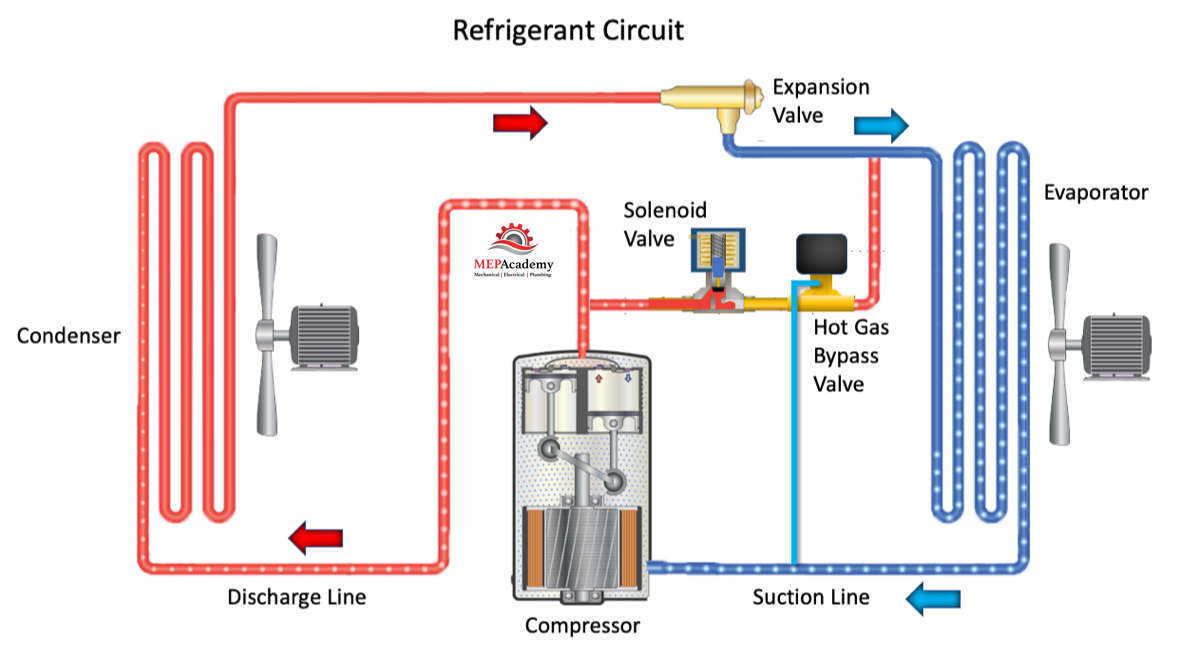
During a pump down cycle, you don’t want this valve to interfere with lowering the evaporator pressure, so a solenoid valve is installed ahead of the Hot Gas Bypass Valve. When the pump down cycle is initiated, the solenoid stops the flow to the Hot Gas Bypass Valve preventing it from bypassing hot gas into the evaporator.
The use of Hot gas Bypass is considered old technology, as it’s more energy efficient to use multiple compressors or variable capacity compressors.
How do Solenoid Valves Work?
An electrical coil within the solenoid valve housing creates an electromagnetic field when energized. The magnetic field induces the opposite polarity in the metal plunger which can be made of iron or steel. Because opposite magnetic poles attract, the plunger will be pulled up into the coil within housing causing the valve to open.
If electrical power remains supplied to the coil, the valve will remain open. This is how a normally closed valve works. When the coil is de-energized the magnetic field disappears and the plunger falls by gravity, or a spring pushes the plunger to close the valve. The coil can use line or low voltage power to be energized.
So, it’s the magnetic field that operates the valves and creates the valve to open.
Solenoid valves are available in the normally open or normally closed position. The designation of normally open or normally closed applies to the position of the valve with no power applied, hence its normal position.
Normally Closed Solenoid Valves
The normally closed solenoid valve is the more commonly used form. The normally closed solenoid valve opens when power is applied to the solenoids coil windings. When no electrical power is applied the valve will remain closed.
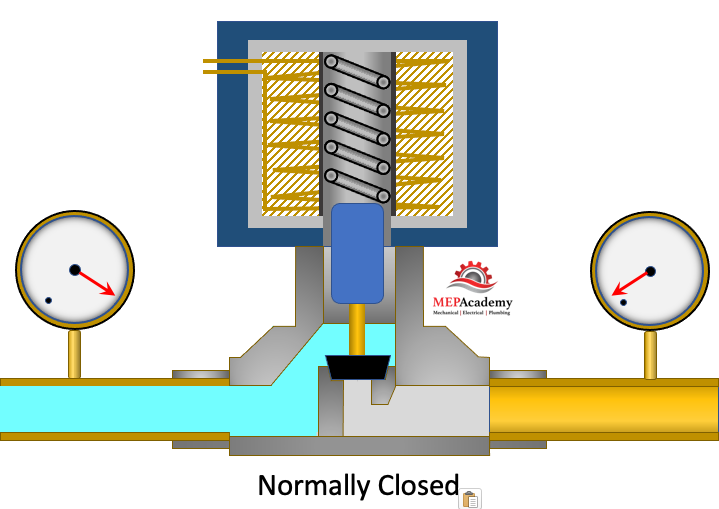
With a normally closed valve the spring keeps the valve closed when no electricity is applied to the coil. When the coil receives power, the magnetic field induces an opposing magnetic charge to the plunger causing it to be pulled upward into the heart of the magnetic field, opening the valve.
When the power is shutoff the magnetic field disappears allowing the spring to push the plunger downward closing the valve.
Solenoid Valve – Normally Open
The normally open solenoid is always open until power is applied to its coil windings. This is the type used for refrigeration pump down, as you want the flow of refrigerant to be unhindered until its time to activate the solenoid valve and force closed the valve.
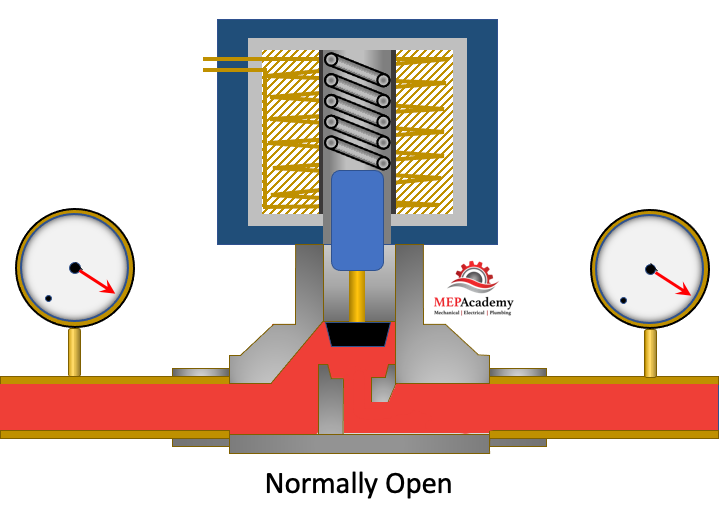
When power is applied to the coil it pushes the plunger downward instead of pulling upward. This causes the plunger to close the valve. When power is shutoff to the coil, the spring will force the plunger upward opening the valve.







