HVAC School for Technicians. In this article we’ll cover what you can expect to be paid as an Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Technician, the education required, and what you can be expected to do while at work.
If you prefer to watch the Video of this presentation, then scroll to the bottom.
Air Conditioning and Heating systems play a crucial role in controlling the temperature, humidity, and air quality within residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Essential items such as food and medicine rely on refrigeration to prevent spoiling. Skilled technicians are responsible for the repair, maintenance, and installation of heating, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems.
Average Pay for a HVACR Technician
How much money can you make as an Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Technician?
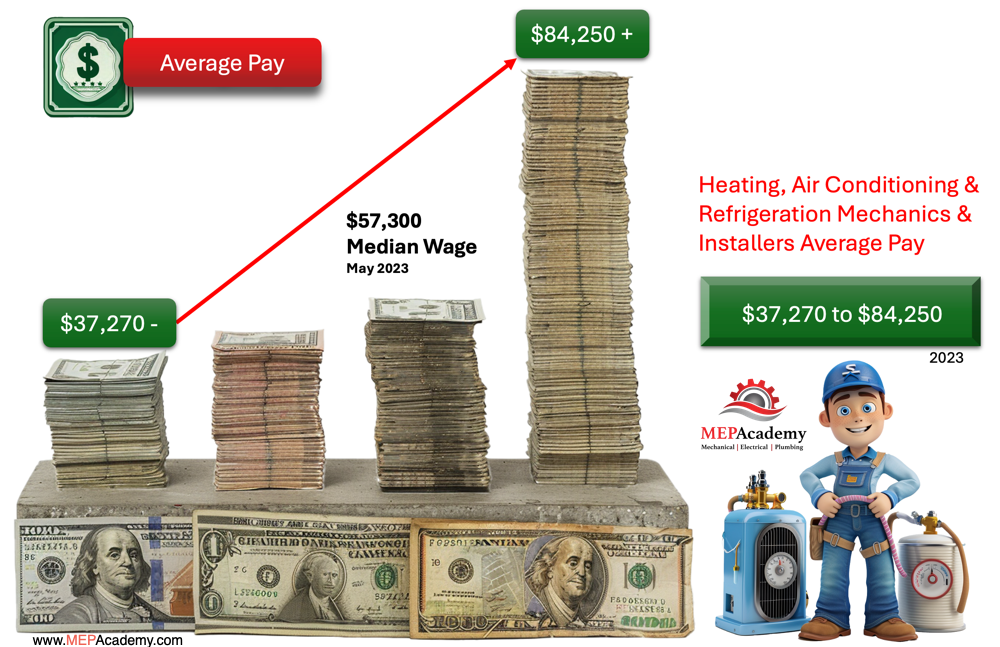
Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Technicians get paid anywhere from $37,270 and less for the bottom 10% of workers, to more than $84,250 per year for the top 10% of earners according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics for 2023. The median wage was $57,300 in May 2023.
Most of the HVACR technicians work at full time positions, which may require evening and weekend hours. During peak seasons for heating or cooling, HVACR technicians can be requested to work overtime or irregular hours to help customer get their systems up and running after they breakdown. Obviously working overtime will increase your hourly pay.
Current Job Opportunities
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the Employment of heating, air conditioning, and refrigeration mechanics and installers is projected to grow 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, faster than the average for all occupations.
About 37,700 openings for heating, air conditioning, and refrigeration mechanics and installers are projected each year, on average, over the decade. Many of those openings are expected to result from the need to replace workers who transfer to different occupations or exit the labor force, such as to retire.
EDUCATION
While a high school diploma or equivalent may be the minimum requirement for many entry-level positions, obtaining formal education through a vocational school, community college, or technical institute can provide a solid foundation. Some of these vocational programs even take individuals lacking a high school diploma. Look for programs specifically focused on HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) or refrigeration technology.
Training Programs
Consider enrolling in an apprenticeship or training program offered by trade associations, Unions, Technical Schools, or HVAC companies. These programs often combine classroom instruction with hands-on experience under the guidance of experienced technicians. If accepted into a Union apprenticeship program you’ll be paid while learning.

Certification
Although not always mandatory, obtaining certification can enhance your credibility and job prospects. A Certificate of Achievement can be secured from an HVACR technical school in 2 years or less. This can shorten the period from entering school to getting a full-time job. After your first semester in a technical school, you could seek a part-time apprenticeship job with a local HVAC contractor.
The most widely recognized certification for HVAC technicians in the United States is offered by North American Technician Excellence (NATE). Other certifications may be available depending on your location and specialization.
Licensing
In some jurisdictions, HVAC technicians are required to obtain a license to work independently. This won’t stop you from working for others. Requirements vary by state or country, so be sure to research the specific licensing regulations in your area. States like California requires a contractor’s license to open your own company and require prior work experience.
Skills Development
Develop a strong understanding of heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems, as well as electrical and mechanical principles. Good problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and the ability to work independently are also important.
Experience
Gain practical experience by working as an apprentice or entry-level technician under the supervision of experienced professionals. This will allow you to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings and develop valuable troubleshooting skills.
Continuing Education
Stay updated on advances in HVAC technology and industry regulations through continuing education courses, workshops, and seminars. This will ensure that your skills remain relevant and competitive in the field.
By following these steps and continually honing your skills, you can become a competent and successful HVACR technician.
The Work of an Air Conditioning & Refrigeration Technician
Air conditioning and refrigeration technicians, install, maintain, and repair, heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems. These systems are found in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.

This could include work on small residential systems such as split systems or packaged units. Also large chilled water plant equipment such as air-cooled and water-cooled chillers. Chillers provide cold water that gets pumped throughout the building. Or you could be working on commercial boilers that provide heating. There are various additional commercial systems that add an extra layer of complexity to the job.
Their responsibilities typically include:
Installation
Installing new HVACR systems, including air conditioners, furnaces, heat pumps, Variable Refrigerant Flow Systems, refrigeration units, and ventilation systems. Installing these systems in accordance to specifications and building codes.

This includes learning how to cut and prepare copper tubing ends, including flaring, swaging, and brazing.
Maintenance
Performing routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning coils, replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, lubricating moving parts, and inspecting electrical connections. This ensures systems operate efficiently and safely.
Repair
Diagnosing and troubleshooting problems with HVACR systems, including issues with components such as compressors, motors, thermostats, boilers, and pumps. This includes making the necessary repairs to restore functionality.
Refrigerant Handling
Handling refrigerants safely and in compliance with environmental regulations, including recovering, recycling, and disposing of refrigerants according to industry standards.
Customer Service
Interacting with customers to understand their heating and cooling needs. Providing recommendations for system upgrades or replacements. Ensuring customer satisfaction with the quality of service provided.
Safety Compliance
Adhering to safety protocols and regulations to minimize risks of injury or property damage during installation, maintenance, and repair activities.
Overall, air conditioning and refrigeration technicians play a crucial role in maintaining comfortable and efficient indoor environments, by ensuring that HVACR systems operate effectively and reliably.
Where HVACR Technicians Work
Air conditioning and refrigeration technicians work in a variety of environments, depending on the specific job and industry. Here are some common work environments for HVACR technicians:
Residential Settings
Technicians may work in homes, apartments, and condominiums to install, repair, and maintain heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration systems for individual homeowners or property management companies.
Commercial Buildings
HVACR technicians often work in commercial settings such as office buildings, retail stores, restaurants, and hotels. They may install and service larger HVACR systems to provide climate control for occupants and ensure comfort and productivity.
Industrial Facilities
In industrial settings such as factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants, technicians may install and maintain specialized HVACR systems to regulate temperature and humidity levels for equipment operation and product storage.
Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals, clinics, and medical laboratories require precise temperature and humidity control to maintain a sterile environment and protect sensitive medical equipment. HVACR technicians may work in these facilities to install and service specialized HVACR systems.
Educational Institutions
Schools, colleges, and universities rely on HVACR systems to create comfortable learning environments for students and faculty. Technicians may be employed by educational institutions or contracted to provide HVACR services.
Government Buildings
HVACR technicians may work in government buildings such as courthouses, libraries, and municipal offices to maintain climate control systems and ensure the comfort and safety of employees and visitors.
Construction Sites
During new construction or renovation projects, HVACR technicians may work on construction sites to install piping. This includes installing HVACR equipment according to building plans and specifications.
Outdoors
Some tasks, such as HVACR system inspections, maintenance, and repairs, may require technicians to work outdoors, especially when servicing rooftop units or equipment located in outdoor enclosures.
Overall, air conditioning and refrigeration technicians can expect to work in a variety of indoor and outdoor environments. They will encounter different conditions and challenges depending on the specific job and industry. They must be prepared to adapt to different work settings and follow safety protocols. This is to ensure their well-being, and the efficient operation of HVACR systems.







