Outside Air Intake Locations and Air Classifications. In this presentation we’ll learn where outside air intakes can be located and why. We’ll learn what the four classifications of air are, and how they relate to outdoor air intakes, including their Minimum separation distances as shown in ASHRAE 62.1 Table 5-1.
If you prefer to watch the YouTube version of this presentation then scroll to the bottom or click on this link. Outside Air Intake Locations and Air Classifications
ASHRAE 62.1-2019 Air Classifications
ASHRAE ranks air according to the level of contaminants in the air and the level of sensory irritation. The classification extends from Class 1 which is considered low contaminant level, to class 4 which is highly objectionable. Class 1 is the cleanest air classification, while class 4 is the worst.
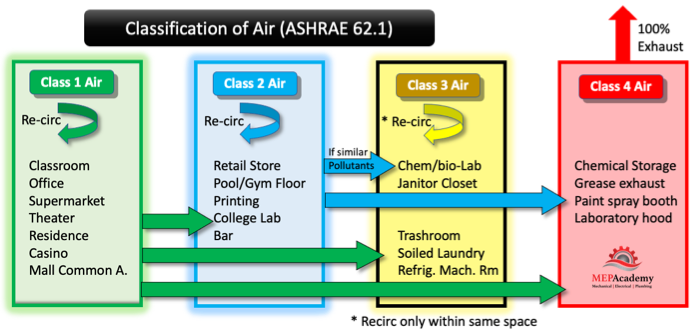
Class 1 Air with low contaminant concentrations, low sensory-irritation intensity, an inoffensive odor is suitable for recirculation or transfer to any space in classes 1 through 4.
Class 2 air can be recirculated within the same space of origin, or transferred to another Class 2 or 3 Space used for similar purposes or has similar pollutants. Class 2 air can be transferred to class 4 spaces. Class 2 air can’t be transferred to the cleaner class 1 air spaces. Air is almost always transferred from the cleaner space to the dirtier classification of air, unless some method of air cleaning is used.
Class 3 air can be recirculated only within the same space of origin, and can’t be recirculated or transferred to any other space. Class 4 air can’t be recirculated or transferred to any space.
According to ASHRAE 62.1 Table 5-1
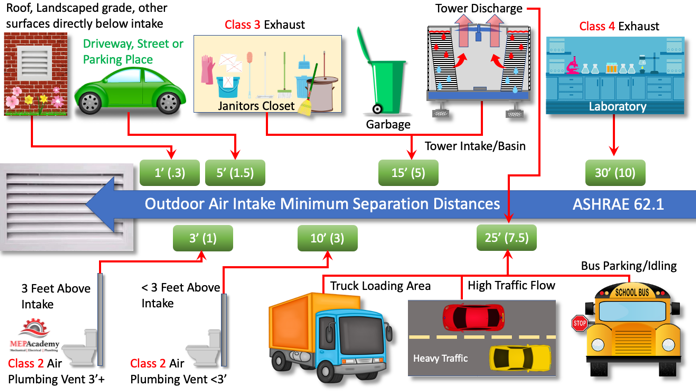
Per ASHRAE standard 62.1 the following minimum distances need to be maintained from the location of any Outdoor Air Intake. A minimum distance of 25 feet (7.5 meters) needs to be maintained between an Outdoor air intake and locations where Buses park or idle. A minimum of 5 feet (1.5 meters) is required between intakes and driveways, streets or parking places.
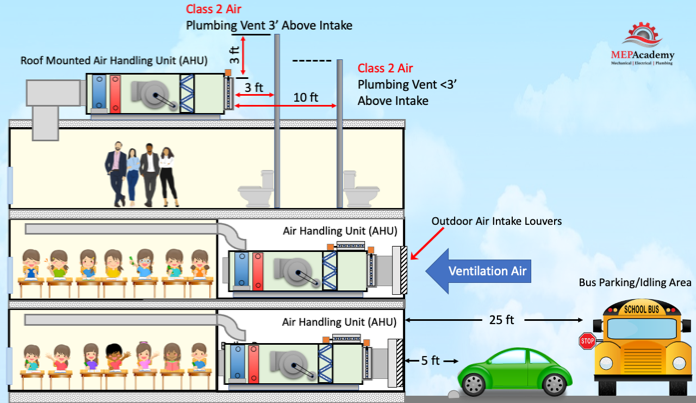
Any Class 2 exhaust or plumbing vent terminating less than 3 feet (1 meter) above the level of the outdoor intake is required to be located a minimum of 10 feet (3 meters) away. Class 2 Air has moderate contaminant concentrations, mild sensory-irritation intensity, or mildly offensive odors. (Class 2 air also includes air that is not necessarily harmful or objectionable but that is inappropriate for transfer or recirculation to spaces used for different purposes.)
A plumbing vent terminating at least 3 feet (1 meter) above the level of the outdoor intake is required to be located a minimum of 3 feet (1 meters) away.
Continuing with ASHRAE Table 5-1, we have the requirement to keep Outdoor intakes a minimum of 25 feet (7.5 Meters) away from truck loading docks. A minimum of 25 feet (7.5 meters) must be kept between any highway with high traffic volume and an intake.
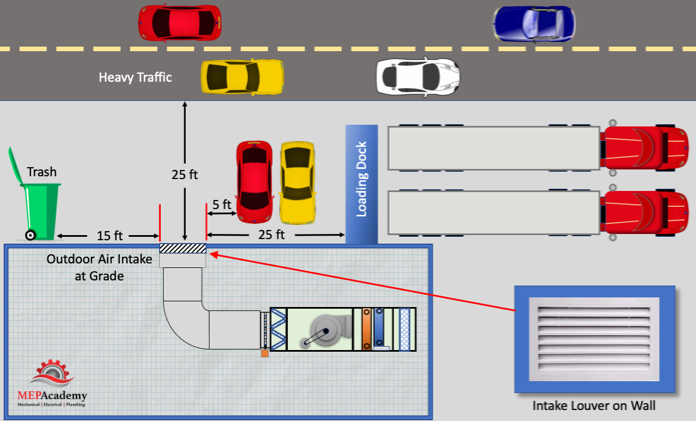
All around the world offices, schools, homes, and hospitals are built near highways and major roadways. Pollution from traffic has been documented to cause serious health problems, from physical to cognitive. The level of pollutants from traffic varies based on proximity to road and level of traffic. There are two sources of contaminants from traffic, the tail-pipe emissions and the physical wear and degradation of brakes and tires. You could also include noise as having adverse effects on health.
Any locations where trash is stored or picked up, including dumpsters will need to be at least 15 feet (5 meters) away from any outdoor intake.
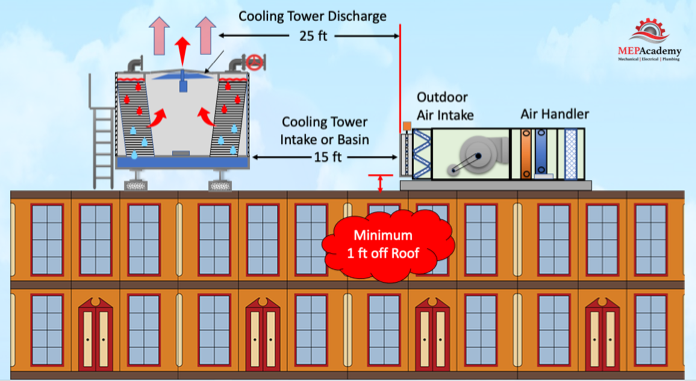
If you have a Outdoor Air intake near a cooling tower than the requirements are that the tower basin or intake to the tower needs to be a minimum of 15 feet (5 meters) away from the Outdoor Air Intake. The discharge of the cooling tower needs to be at least 25 feet (7.5 meters) away.
Potential contaminant sources are restricted on how close they can be to an air intake based on their classification. Air is classified based on the source of the contaminant, from class 1 to class 4.
Here is a Class 3 exhaust shown the minimum distance of 15 feet (5 meters) away from this air handlers outdoor air intake. Class 3 is Air with significant contaminant concentration, significant sensory-irritation intensity, or offensive odor that is suitable for recirculation within the same space. Class 3 air is not suitable for recirculation or transfer to any other space.
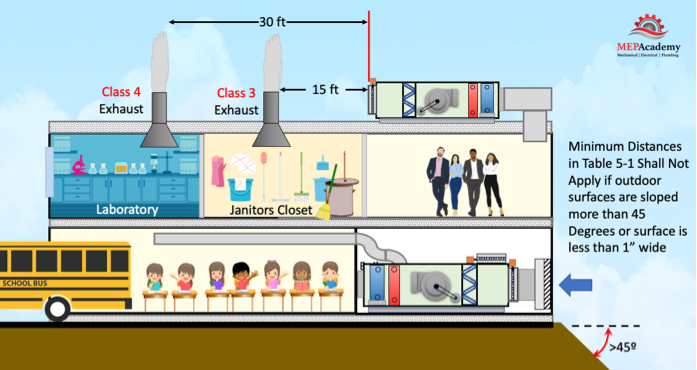
There is a laboratory exhaust system in this building which is classified as Class 4 air, which means its minimum distance to intakes is 30 feet (10 meters). Class 4 Air has highly objectionable fumes, gases, or potentially dangerous particles, bioaerosols, or gases at concentrations high enough to be considered harmful. Class 4 air is not suitable for recirculation or transfer within the space or to any other space.
There is the requirement to maintain at least a 15 foot (5 meter) distance from a drive in queue to any outdoor air intake.
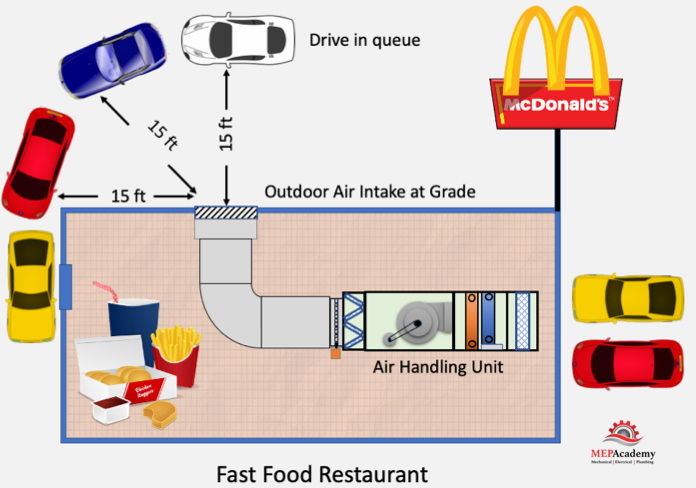
When locating outside air takes its important to consider the possible sources of contaminants from the surroundings. ASHRAE 62.1-2019 4.3 requires an outdoor air quality investigation be conducted and documented. The survey should document any observation of odors, irritants, visible plumes, visible air contaminants, and include description of sources of vehicle exhaust on site and from adjoining properties.
ASHRAE Table 5-1 Air Intake Minimum Separation Distance
This table reflects the minimum distances that an exhaust or contaminant must be in reference to the outdoor air intake. There is an analytical method which can be used as an alternate procedure for determining separation distances between exhaust outlets and outdoor air intakes located in Appendix “B” of the standard.
Just because you maintain these distances doesn’t mean you will avoid entrainment, there is no magic to these distances. Other factors like wind direction and strength, building geometry and the exhaust design could have an adverse effect.
Roof, Landscaped Grade, or Another Surface Directly Below Intake.
If you live where snow is common, then the intake will need to be designed with the distances calculated from the average snow level. This snow average snow depth will be considered the ground level for distance calculations.
Summary
It’s important that air intakes be located safely away from sources of contaminants that could affect the occupant’s health. Outdoor air intakes provide fresh air for building occupants. The location and design of these intakes needs to include protection from contaminants, weather, such as rain, snow, puddling of water, wind-driven rain, and snow.







