Maintaining uninterrupted electrical power is very important for some facilities and processes. Think of a hospital. What would happen if the power went out during a surgery? What would happen to a patient connected to oxygen or life support machine dependent on electricity?
If you prefer to watch the video of this presentation, the scroll to the bottom.
Whether it’s a hospital, a laboratory, a manufacturing facility, or any other critical infrastructure, a sudden utility power outage can have severe consequences. This is where Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) can ensure the seamless transition to backup power sources. In this article, we’ll explore how ATS is employed to maintain power during utility outages and why they are a fundamental part of various construction projects.
How Automatic Transfer Switches Work
Automatic Transfer Switches are devices that monitor the quality of the primary power source, which is typically the utility grid, and automatically switch to an alternative power source when an outage is detected. Here’s how they work:
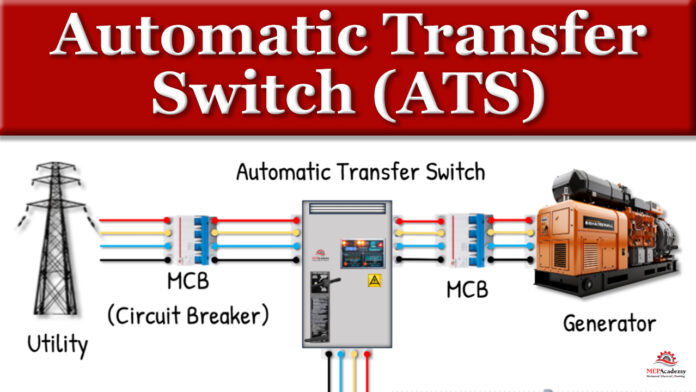
An ATS system is designed to connect to two power sources: the primary utility power and a secondary backup power source, often a generator.
During normal operation, the ATS connects the load to the primary power source. The controller keeps a close eye on the quality of this power source.
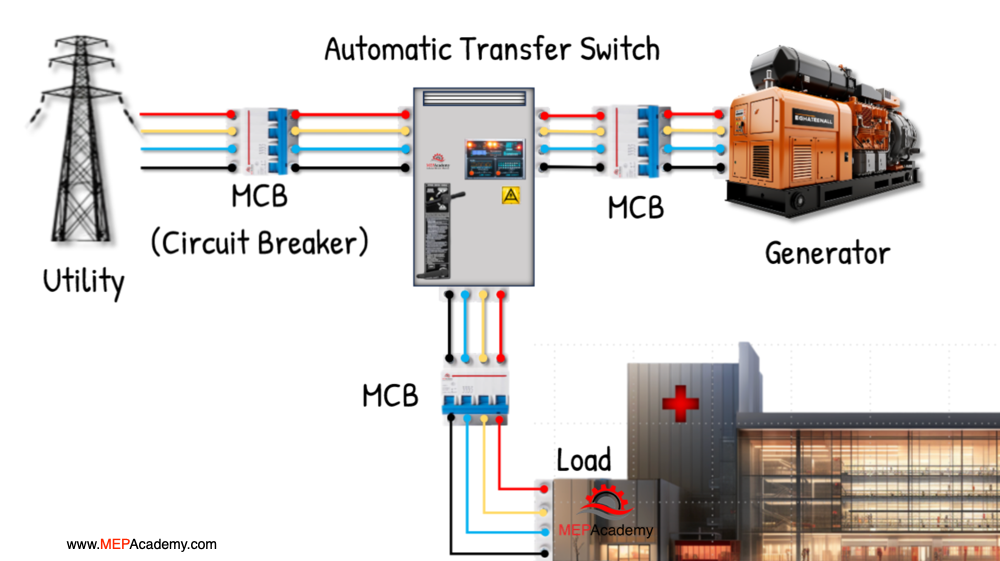
ATS systems are equipped with sensing devices that continuously monitor the voltage and frequency of the primary power source. When the controller detects an interruption in the primary power supply, it automatically initiates a transfer to the secondary source, typically a generator. This swift response is critical for critical applications such as hospitals and data centers. This transfer occurs in less than 1 second.
Switch Mechanism
The heart of the ATS is its switch mechanism, which is responsible for making and breaking electrical connections. It ensures that only one power source can be connected at a time, preventing any back feeding of power.
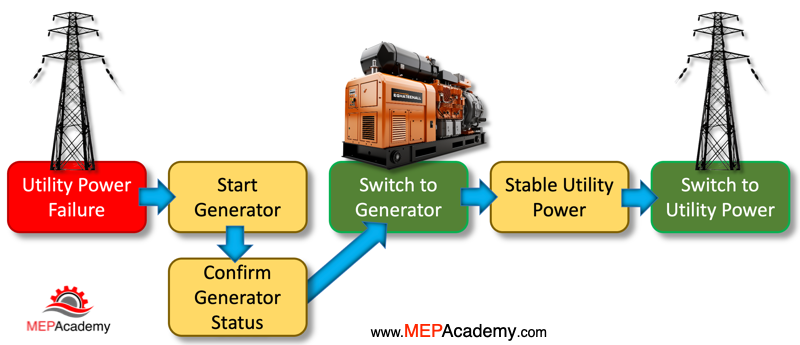
Before making the transfer to the secondary source, the ATS ensures that the generator’s output matches the utility power in terms of voltage, frequency, and phase. This synchronization is vital to protect sensitive equipment from damage.
Once the utility power is restored and stable, the ATS automatically switches the load back to the primary source, ensuring that the backup source is used only when necessary.
The Role of ATS in Commercial Construction
1. Hospitals: In hospitals, where uninterrupted power is critical for life-saving equipment, ATS systems ensure that surgeries, intensive care units, and other essential functions continue without interruption during power outages.
2. Laboratories: Research facilities and laboratories rely on precise and stable power for experiments and sensitive equipment. ATS systems guarantee that experiments aren’t compromised due to power disruptions.
3. Manufacturing Facilities: Manufacturers can’t afford production downtime due to power outages. ATS keeps assembly lines running smoothly and avoids costly interruptions.
4. Data Centers: Data centers house mission-critical data, and even a brief power interruption can lead to data loss. ATS is essential in these facilities to maintain uninterrupted operation.
5. Hotels: In the hospitality industry, guest comfort and safety are top priorities. ATS systems ensure that guests aren’t inconvenienced by power disruptions.
Conclusion
Automatic Transfer Switches are unsung heroes in the world of commercial construction. They play a vital role in ensuring uninterrupted power in critical applications, from hospitals to laboratories, manufacturing facilities, data centers, and beyond. For those in the construction industry, understanding the importance of ATS systems is key to delivering projects that meet the highest standards of reliability and safety. These unassuming devices are the backbone of power continuity in our modern world, making sure that when the lights go out, the show goes on.