Refrigerant recovery is the process of removing refrigerant from a refrigeration or air conditioning system for recycling, reclamation, or disposal. It is an essential step in the maintenance and repair of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Proper refrigerant recovery is important to protect the environment and comply with regulations.
Here are some key steps involved in refrigerant recovery:
- Prepare the equipment: The recovery equipment should be properly maintained and calibrated before starting the recovery process to make sure everything is operating properly. The hoses and fittings should also be checked for leaks.
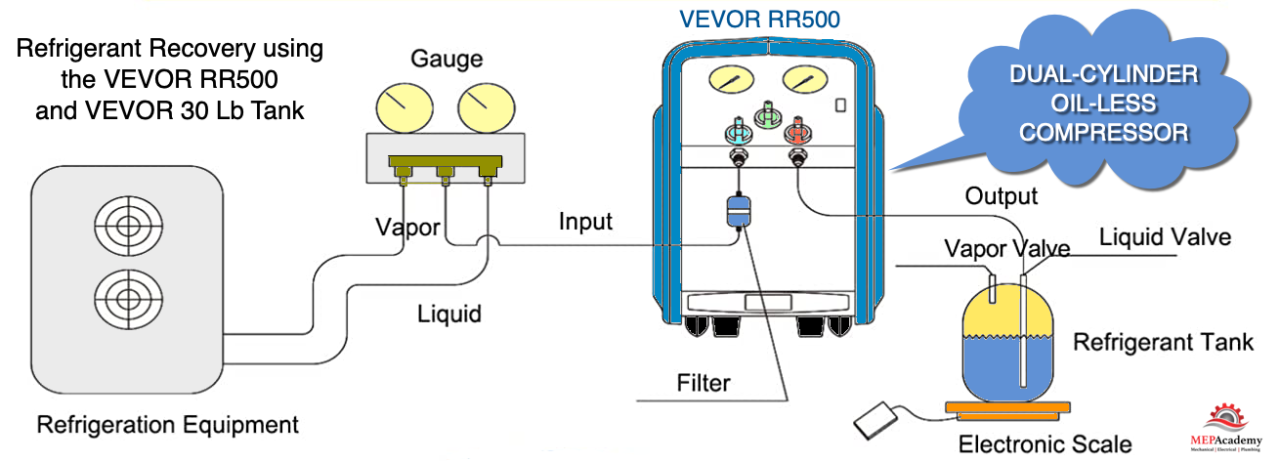
- Refrigerant Recovery: The refrigerant is removed from the system using a recovery machine like the Vevor RR500 shown here which uses 110-120v 60 Hz power with a powerful 3/4 Hp dual-cylinder oil less compressor. The refrigerant is typically pumped into a recovery cylinder for storage and transportation, like the Vevor 30 Lb. tank shown here which comes prefilled with a trace amount of nitrogen to guard against corrosion and has a working pressure of 400 psi. The recovery equipment should be connected to the system using the appropriate hoses and fittings. The hoses should be purged of air before connecting to the system.
- Recover the refrigerant: The refrigerant should be recovered from the system using the Vevor recovery equipment. The amount and type of refrigerant recovered should be documented for compliance with regulations including the EPA’s mandatory section 608. Section 608 states that the Technicians disposing of appliances containing between 5 and 50 pounds of refrigerant must keep records of the disposal.
- Refrigerant Storage: The recovered refrigerant should be stored in a properly labeled container and transported to a recycling facility for reuse or disposal. The recovered refrigerant is stored in a DOT-approved cylinder that is designed for refrigerant storage. The cylinder must be properly labeled with the type of refrigerant, the amount of refrigerant, and the date of recovery.
- Refrigerant Disposal or Recycling: The recovered refrigerant can either be properly disposed of or recycled for reuse. Disposal methods can vary depending on local regulations, but typically involve sending the refrigerant to a licensed facility for destruction. Recycling involves filtering and cleaning the refrigerant to remove impurities before it can be used again.
- Clean up: Any residual refrigerant and contaminants should be properly disposed of, and the recovery equipment should be cleaned and stored properly.
Overall, proper refrigerant recovery is an important process for protecting the environment, complying with regulations, and reducing costs associated with refrigerant replacement. It’s important to follow proper procedures and regulations when recovering, storing, and disposing of refrigerants.
It’s important to note that refrigerant recovery should only be performed by trained professionals who have the proper equipment and knowledge of regulations. Refrigerants are harmful to the environment and can cause harm if not handled properly.
Here are some key considerations for refrigerant recovery.
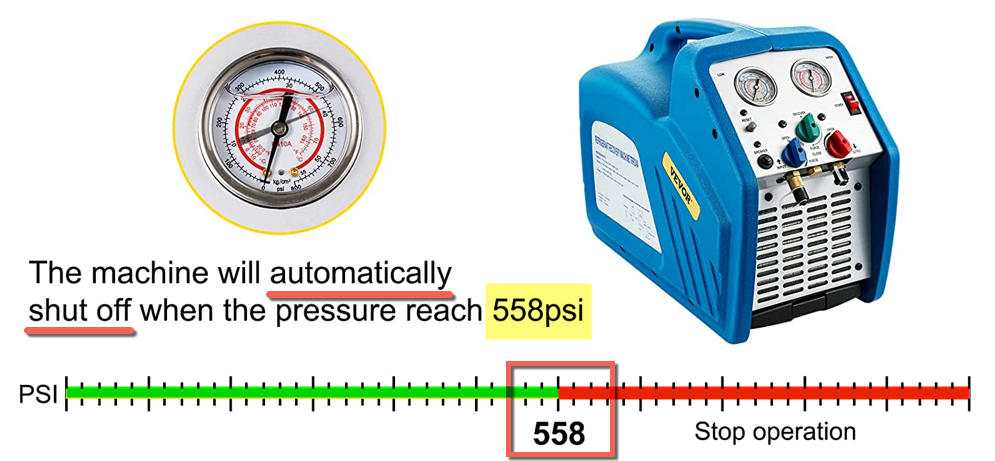
- Safety: Refrigerants can be hazardous to human health and the environment, so safety should be the top priority during the recovery process. Technicians should wear appropriate personal protective equipment, and the recovery equipment should be well-maintained and tested for leaks. The Vevor refrigerant recovery tank is included with a pressure relief valve that will automatically relieve any pressure exceeding the tanks working pressure. The Vevor refrigerant recovery machine RR500 has an intake and discharge gauge that allows you to always observe the pressures. It includes a high-pressure cut-off switch that automatically shuts down the machine if the internal pressure is higher than 558 psi to ensure secure operation.

Technicians serving AC and refrigeration equipment must pass a certification exam to maintain, service, repair, or dispose of appliances containing refrigerants.
- Recovery Equipment: The recovery equipment used should be compatible with the type of refrigerant being recovered. The equipment should also be properly sized for the system being serviced, and technicians should follow the manufacturer’s instructions for its use. The Vevor 30 lb. capacity refrigerant recovery tank can handle a wide range of refrigerants including R134A, R-22, R-12, R410A, R404A, R502, R1234YF, and R32.
- Recovery Techniques: There are two primary techniques for refrigerant recovery: liquid recovery and vapor recovery. Liquid recovery is used for systems that have a high percentage of liquid refrigerant, while vapor recovery is used for systems with mostly vapor refrigerant. Technicians should be trained in both techniques and choose the appropriate method based on the system being serviced. The Vevor RR500 recovery machine can quickly recover vapor and liquid refrigerants using a maximum recovery speed of 1750 rpm.
There are three valves on the Vevor RR500 refrigerant recovery machine that provides multiple adjustment modes including liquid recovery, vapor recovery and self-purge modes.

- Record-Keeping: Proper documentation is important for tracking the amount and type of refrigerant recovered. Technicians should keep accurate records of the amount of refrigerant removed, the type of refrigerant, and the date of recovery.
- Recycling or Reclamation: Recovered refrigerant can be recycled or reclaimed for reuse in other systems. Technicians should follow EPA guidelines for handling, storing, and transporting recovered refrigerant for recycling or reclamation. Recovered refrigerant may not be resold unless it has been reclaimed by a certified reclaimer or is being transferred to equipment belonging to the same owner.
- Disposal: If refrigerant cannot be recycled or reclaimed, it must be properly disposed of according to EPA regulations. Technicians should follow the guidelines for disposal and keep accurate records of the amount and type of refrigerant disposed of.
- Environmental Protection: Refrigerants such as CFCs, HCFCs, and HFCs are known to deplete the ozone layer and contribute to global warming. Proper recovery and disposal of these refrigerants helps to protect the environment and prevent the release of harmful gases into the atmosphere.
- Legal Compliance: In many countries, it is illegal to release refrigerants into the atmosphere. Proper recovery and disposal are required by law to comply with environmental regulations so make sure you use a recovery machine and recovery tank like the ones provided by Vevor. Section 608 of the EPA’s Clean Air Act prohibits the knowing release of refrigerant during maintenance, service, repair, or disposal of air conditioning and refrigerant equipment.
- Cost Savings: Recovered refrigerants can be recycled and reused, which can result in cost savings compared to purchasing new refrigerants. The cost of refrigerants has increased dramatically with the phaseout of production of some refrigerants.
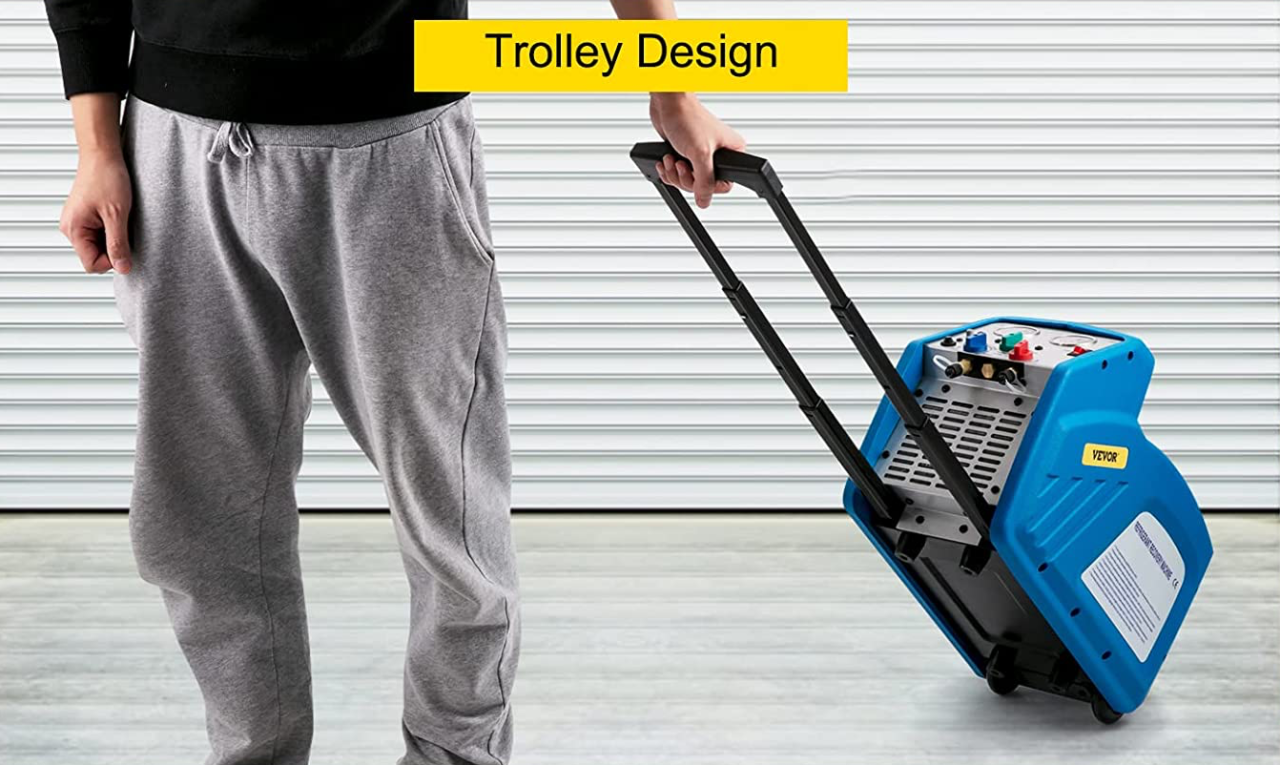
- Portable and Handy: The Vevor RR500 refrigerant recovery machine is compact and lightweight making it convenient to carry or roll around using the trolley handle and wheels.

Overall, proper refrigerant recovery is essential for the safe and efficient operation of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Technicians should follow best practices for safety, equipment, techniques, record-keeping, and proper handling of recovered refrigerant.
Checkout Refrigerants here







