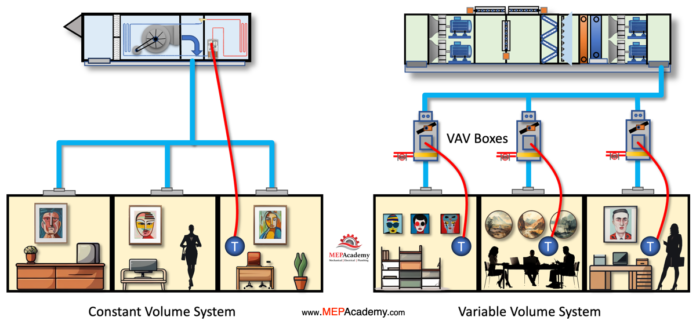
Choosing the Right HVAC System: When to Use VAV vs. Constant Volume Systems
Selecting the appropriate HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system for your building is a critical decision that can impact energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and operating costs. Two common options are Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems and Constant Volume systems. In this video, we’ll help you understand when it’s best to use a VAV system or a Constant Volume system, depending on your specific requirements and goals.
If you prefer to watch the video version of this presentation, then scroll to the bottom.
VAV vs. Constant Volume Zoning Differences
Efficient zoning can make a world of difference in terms of energy consumption, comfort, and cost savings. When comparing Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems to Constant Volume systems, it’s essential to understand the significant zoning differences between these two approaches. In this video, we’ll delve into the nuances of zoning in VAV and Constant Volume systems and how they impact your building’s HVAC performance.
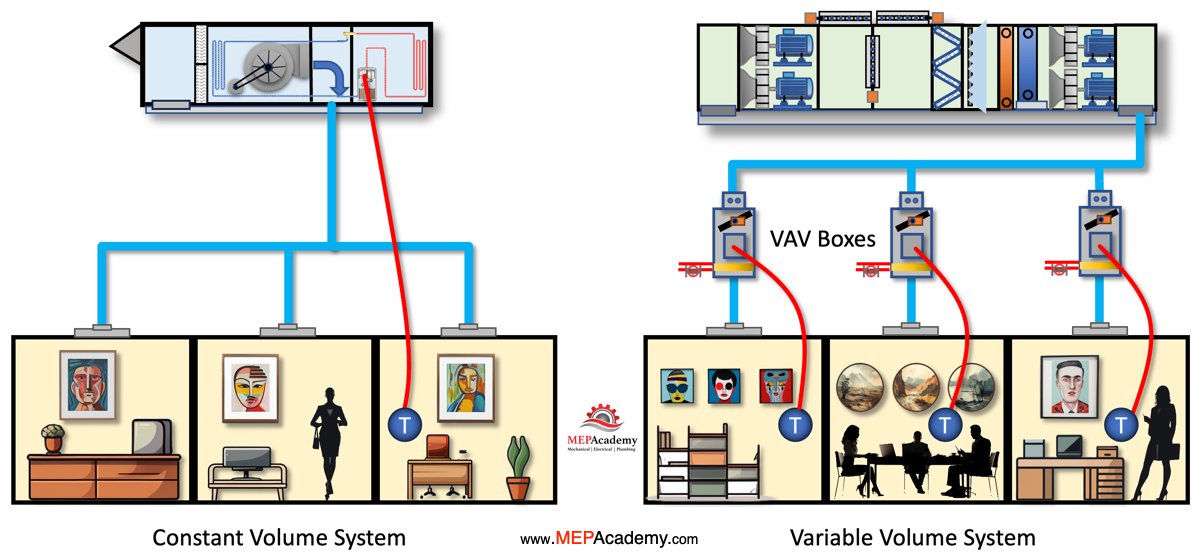
Zoning in Constant Volume and VAV Systems
VAV Individual Zone Control
Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems excel in providing precise zoning control. Here’s how zoning works in VAV systems:
VAV systems allow for individual temperature control in various zones or spaces within a building. Each zone has its own VAV box, which modulates the airflow to meet specific heating and cooling demands. As you can see in this diagram each room has its own controller and can determine whether they want heating or cooling.
Zoning in Constant Volume Systems
Constant Volume systems have limitations when it comes to zoning:
In Constant Volume systems, the same airflow is delivered to all zones simultaneously. This lack of individual control can lead to variations in temperature and comfort levels. Constant Volume systems struggle to adapt to changes in occupancy and temperature requirements within different zones. They are less suited for buildings with diverse thermal loads. You can see in this diagram that all rooms have to be in either cooling or heating mode, there is no option foe one room to be in cooling while another is in heating mode.
Temperature and Air Volume Control
With a VAV system the temperature and occupancy sensors continuously monitor conditions in each zone. The VAV system adjusts airflow and temperature, ensuring that comfort levels are maintained in each separate zone.
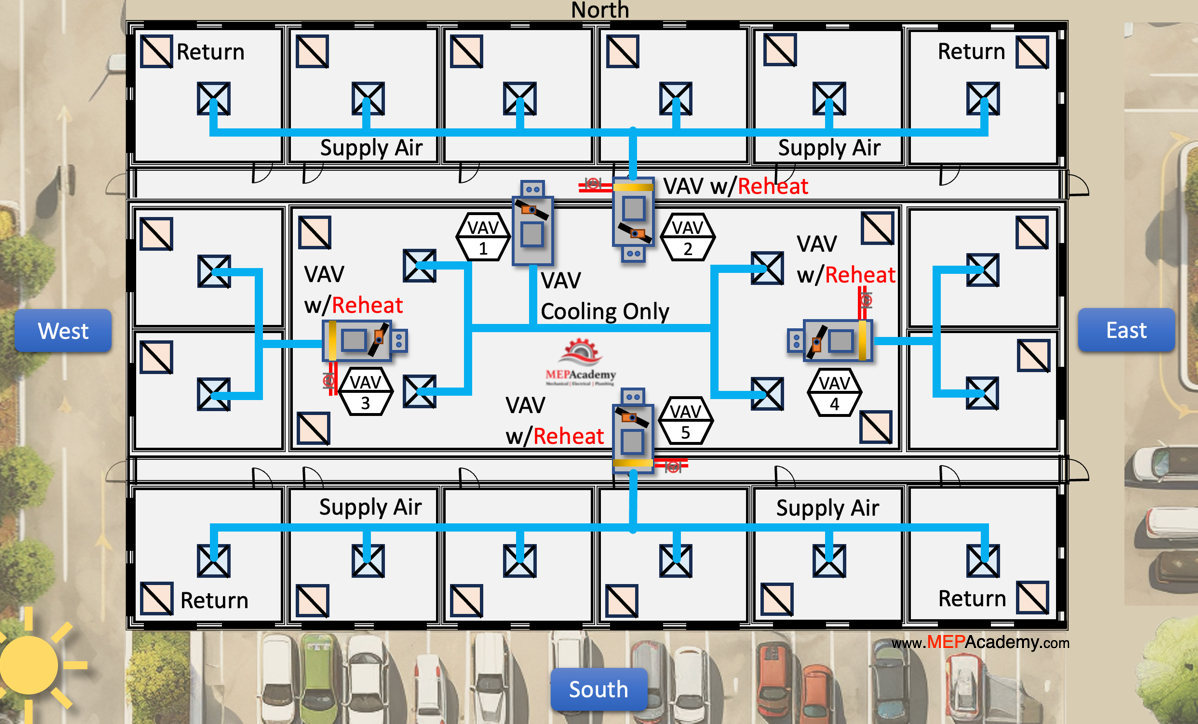
With a constant volume system, the controller is in one of the spaces which can cause problems for other spaces if the room with the controller is unoccupied. This is when comfort complaints occur.
Energy Efficiency
Zoning in VAV systems contributes to energy efficiency by delivering conditioned air precisely where and when it’s needed, reducing unnecessary heating and cooling.
Constant Volume systems maintain a consistent airflow, even when zones require less heating or cooling. This inefficiency can lead to higher energy consumption and costs.
VAV System Benefits of Effective Zoning
Efficient zoning, as seen in VAV systems, offers several advantages:
Customized Comfort
Occupants enjoy personalized comfort levels in each zone, enhancing satisfaction and productivity.
Energy Savings
Zoning reduces unnecessary energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Optimized Equipment Lifespan
HVAC equipment experiences less wear and tear when only operating as needed, potentially extending its lifespan.
Improved Air Quality
Better control over airflow can contribute to improved indoor air quality by minimizing temperature variations and balancing humidity levels.
When to Use a VAV System
Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems are versatile and energy-efficient, making them a popular choice for various applications:
1. Large and Diverse Spaces: VAV systems shine in buildings with multiple zones and varying occupancy levels, such as office buildings, shopping centers, or hotels. They can adapt airflow and temperature settings to meet specific zone requirements.
2. Energy Efficiency Goals: When prioritizing energy efficiency and sustainability, VAV systems are the preferred option. They minimize energy consumption by supplying only the necessary airflow to each zone, reducing operating costs and carbon emissions.
3. Occupant Comfort Matters: If maintaining precise temperature control and occupant comfort is crucial, VAV systems offer superior performance, ensuring consistent comfort levels throughout the building.
4. Cost Savings Over Time: While VAV systems may have a higher initial cost due to their complexity, they offer substantial long-term savings through reduced energy bills and extended equipment lifespan.
When to Use a Constant Volume System
Constant Volume systems have their place in certain scenarios:
Smaller and Simpler Spaces
In smaller buildings or spaces with consistent occupancy and minimal temperature variations, Constant Volume systems can be cost-effective and straightforward to install.
Limited Budget
If you have budget constraints and the building’s requirements align with the capabilities of a Constant Volume system, it may be a more economical choice upfront.
Minimal Zone Control Needed
Buildings with uniform temperature and airflow requirements throughout can benefit from the simplicity of Constant Volume systems.
Ease of Maintenance
Constant Volume systems tend to have lower maintenance costs due to their straightforward design, making them suitable for facilities with limited maintenance resources.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting between VAV and Constant Volume systems involves a careful analysis of your building’s specific needs, goals, and constraints. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help you make the right choice:
1. Evaluate Building Size and Complexity: Assess the size, layout, and diversity of your building’s zones to determine whether VAV or Constant Volume systems are better suited.
2. Define Energy Efficiency Objectives: If energy efficiency and sustainability are top priorities, VAV systems are likely the better choice.
3. Consider Comfort Requirements: Think about occupant comfort expectations. VAV systems excel in delivering precise comfort control.
4. Analyze Initial Budget and Long-Term Costs: Compare the initial investment and long-term operating costs of both systems to make an informed financial decision.
5. Consult with HVAC Experts: Seek guidance from HVAC professionals who can provide tailored recommendations based on your building’s unique characteristics.
Choosing the Right Zoning Approach
When deciding between VAV and Constant Volume systems, consider your building’s size, layout, occupancy patterns, and energy efficiency goals. Effective zoning is a critical factor in creating a comfortable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly indoor environment.
While Constant Volume systems may have their place in smaller, simpler buildings, VAV systems offer superior zoning capabilities for larger, more complex structures with diverse temperature needs. Consulting with HVAC professionals can help you make an informed decision and optimize your zoning strategy to achieve maximum comfort and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
The decision of whether to use a VAV or Constant Volume system should align with your building’s specific needs, budget, and sustainability goals. Both systems have their strengths and weaknesses, so careful consideration and expert guidance will lead you to the HVAC solution that best serves your facility and its occupants.
Zoning differences between VAV and Constant Volume systems can significantly impact your building’s HVAC performance. Precise zoning in VAV systems ensures individual comfort control and energy efficiency, while Constant Volume systems struggle to adapt to varying zone requirements. By understanding these distinctions, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your building’s specific needs and sustainability objectives.