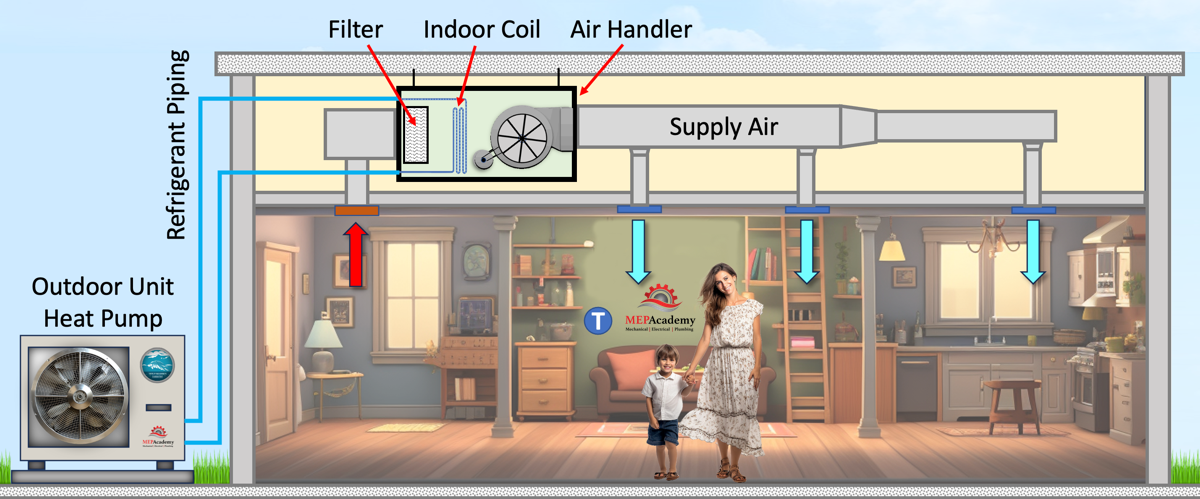
For smaller heating systems or areas, you have several options, with two of the most common choices being heat pumps and furnaces. Both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the pros and cons of each can help you make an informed decision. In this blog post, we’ll compare heat pumps and furnaces to help you determine which one is the right choice for your heating needs.
If you prefer to watch the Video of this presentation, scroll to the bottom.
Heat Pumps
According to the estimates from the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority, Americans bought more than 4.3 million heat pumps in 2022, compared to roughly 3.9 million natural gas furnaces.
Advantages of Heat Pumps
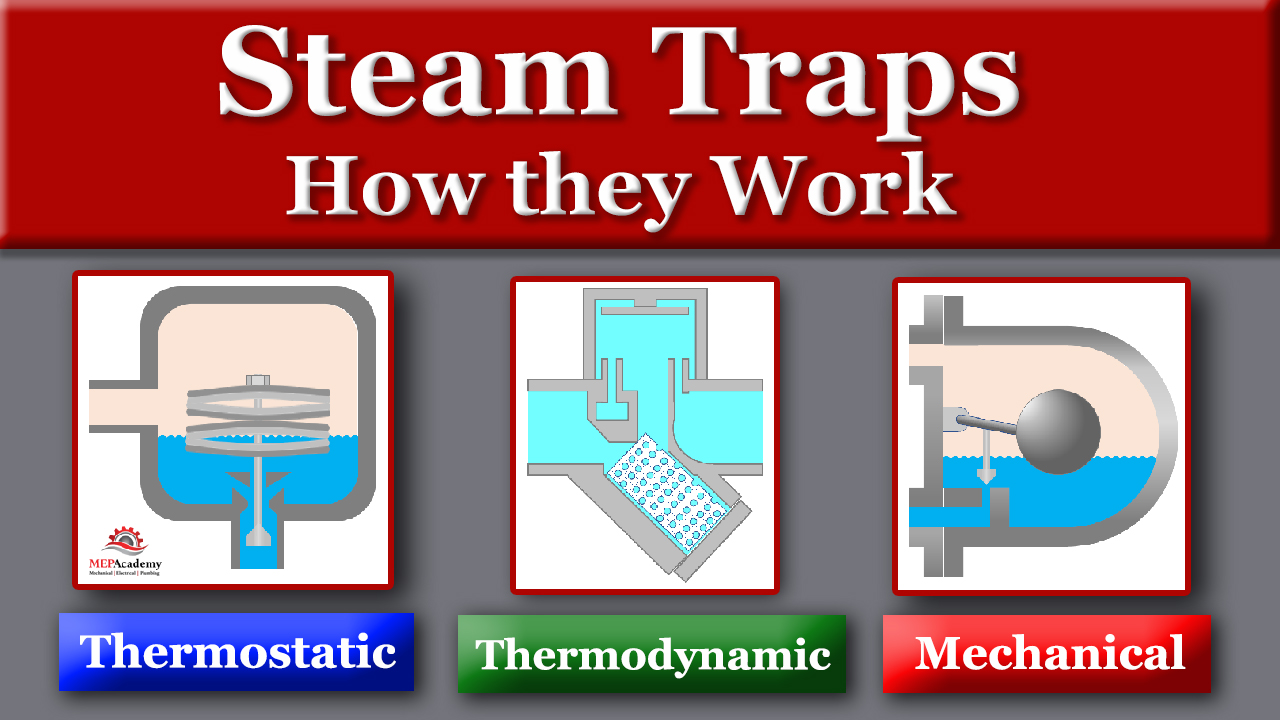
Energy Efficiency
Heat pumps are highly efficient and can provide both heating and cooling. They work by transferring heat from the outside air (or ground) into your home, making them energy-efficient in milder climates. Heat pumps are efficient because they use electricity to transfer heat, rather than create heat by burning a fossil-fuel like natural gas. As the outside air temperature drops, the efficiency will also drop, this is when a high efficiencyfurnace would be a better solution.
Lower Operating Costs
Because they use electricity to move heat rather than generate it, heat pumps can lead to lower lifetime operating cost, especially in regions with moderate climates. Although gas is usually cheaper than electricity, gas furnaces have a greater lifetime operating cost due to maintenance and repair cost. This is dependent on the cost of electricity and fuel in your area.
Year-Round Comfort
Heat pumps offer both heating and cooling functions, eliminating the need for a separate air conditioner in the summer. A heat pump uses a reversing valve, which allows for heat to be absorbed outdoors, even when the weather is cold, and sent to the indoors to provide heating.
Environmentally Friendly
Heat pumps produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to furnaces, contributing to a greener environment. There is a move to eliminate the use of fossil-fuel based appliances in pursuit of zero-emissions. New York has recently passed legislation that would ban fossil-fuel appliances in buildings seven stories or less in 2026. Whether we like it or not, there is a large push to go all electric, and so we should expect more legislation in this area.
Disadvantages of Heat Pump
Upfront Cost
Heat pump installation costs can be higher than that of furnaces, particularly for geothermal heat pump systems. See our video on how geothermal heat pumps work. Additional cost can be attributed to electrical panel and service upgrades for older homes lacking the additional electrical capacity. This could be offset by utility rebates and incentives.
Performance in Extreme Climates
Air-source heat pumps become less efficient in extremely cold weather, requiring a backup heating source in colder climates. It’s important that the heat pump is sized correctly based on the outdoor design temperature for the region.
Heat pumps lose capacity as the temperature drops. This can cause insufficient heating capacity if the outdoor temperature drops below the outside design temperature. At the point on this chart where the two lines meet is where a secondary source of heat such as electric heater can be initiated on these extreme cold days.
Since these extreme temperatures occur only a small percentage of the time, the energy penalty is small. Most areas can benefit from heat pumps except those in extreme climates below -20 F (-29 C).
Maintenance
Heat pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and lifespan. See our article on Heat Pump Maintenance Tips.
Furnaces
Advantages of Furnaces

Effective in Cold Climates
Furnaces, particularly those powered by natural gas or oil, excel in providing consistent and powerful heating, making them suitable for very cold climates. Furnaces are rated by the amount of BTU’s they provide as heat to the space. The heat put out by a natural gas furnace is not affected by the temperature outdoors.
The furnace will always put out the rated BTU’s as long as it’s running properly. For example, if a furnace is rated for 125,000 BTU’s per hour, than it doesn’t matter whether its 65 or 10 degrees out, the furnace still puts out 125,000 BTU’s. This is not the same for heat pumps, who’s capacity is reduced as the weather decreases as previously discussed.
Lower Upfront Costs
Furnaces are often more budget-friendly when it comes to installation costs. As we previously stated heat pumps may require an electrical upgrade.
Quick Warm-Up
Furnaces can heat a home rapidly, providing almost instant comfort.
Longevity
Well-maintained furnaces can have a long lifespan.
Disadvantages of Furnaces
Higher Lifetime Operating Costs
Furnaces tend to have higher lifetime operating costs compared to heat pumps, especially if powered by oil or electric resistance heating. Because of the cost associated with maintenance and repairs, furnaces tend to have higher lifetime cost, although they most often have lower operating cost based on the cost of natural gas in your region.
Some may have Limited Efficiency
Furnaces generate heat, which can be less energy-efficient in moderate climates than heat transfer methods used by heat pumps. Newer condensing furnaces can achieve efficiencies above 90% and are more efficient in extreme cold climates.
Environmental Impact
Furnaces that run on oil, coal or natural gas can have a significant environmental impact due to emissions. As previously mentioned, there is a global move to get away from fossil fuels.
Separate Cooling System
Furnaces don’t provide cooling, so you’ll need a separate air conditioning system if you want both heating and cooling capabilities. There are three main components for a split system gas/electric air conditioner. There is the outdoor condensing unit, the indoor furnace and cooling coil.
In summary, the choice between a heat pump and a furnace depends on your specific needs, climate, budget, and environmental considerations. Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, while furnaces are known for their effectiveness in extreme cold. By evaluating the pros and cons of each system, you can make an informed decision that best suits your home and lifestyle.
If you need help deciding or have questions about heating options for your home, don’t hesitate to reach out to a professional HVAC technician who can provide expert advice tailored to your situation.